Actions are the one of the RDD operation:
Actions:
Actions, which return a value to the driver program after running a computation on the dataset.
Note:
Actions may trigger a previously constructed, lazy RDD to be evaluated.
1)reduce(func):
Aggregate the elements of the dataset using a function func (which takes two arguments and returns one).
Note:
Function should be commutative and associative so that it can be computed correctly in parallel.
Pictorial view:
Example: Python spark:
Example: Scala spark:
2)collect():
Returns all the items in the RDD, as a list to driver program.
Pictorial view:
Example: Python spark:
Example: Scala spark:
3)count():
Returns number of elements in the RDD.
Example: Python spark:
Example: Scala spark:
4)first():
Return the first element in the RDD.
Example: Python spark:
Example: Scala spark:
5)take(n):
Return an array with the first n elements of the RDD.
Example: Python spark:
Example: Scala spark:
6)takeSample(withReplacement:boolean, num:int, [seed]):
Return an array with a random sample of num elements of the dataset, with or without replacement.
Example: Python spark:
Example: Scala spark:
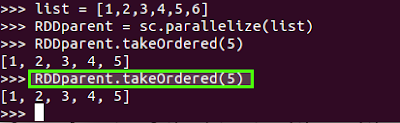
7)takeOrdered(n, [ordering]):
Return the first n elements of the RDD using either their natural order or a custom comparator.
Example: Python spark:
Example: Scala spark:
8)saveAsTextFile(path):
Save RDD as text file, using string representations of elements.
Pictorial view:
Syntax:
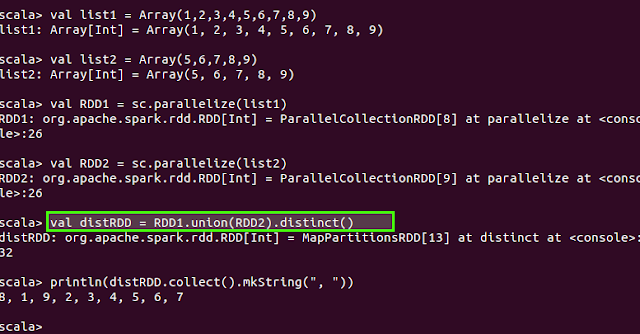
Example: Scala spark:
Since the default parallelism is 4, so during export, the RDD is split into fours partitions on local directory.
9)saveAsSequenceFile(path):
Write the elements of the dataset as a Hadoop SequenceFile in a given path in the local filesystem, HDFS or any other Hadoop-supported file system. This is available on RDDs of key-value pairs.
Example: Python spark:
Example: Scala spark:
10)saveAsObjectFile(path):
Saves RDD as an object fil
Example: Python spark:
Note:
Object file format does not support in python spark.
Example: Scala spark:
11)countByKey():Count the number of elements for each key, and return the result as a dictionary.
Pictorial view:
Example: Python spark:
Example: Scala spark:
12)foreach(func):
To iterate through all the items in RDD and apply function to all.
Note:
Helpful, when we want to insert items in RDD.
Example: Python spark:
Example: Scala spark:
Please click next to proceed further ==> Next
Actions:
Actions, which return a value to the driver program after running a computation on the dataset.
Note:
Actions may trigger a previously constructed, lazy RDD to be evaluated.
1)reduce(func):
Aggregate the elements of the dataset using a function func (which takes two arguments and returns one).
Note:
Function should be commutative and associative so that it can be computed correctly in parallel.
| Actions | Usage |
| i)General Actions | |
| reduce(func) | Aggregate the elements of the dataset using a function func (which takes two arguments and returns one). |
Pictorial view:
Example: Python spark:
Example: Scala spark:
2)collect():
Returns all the items in the RDD, as a list to driver program.
| Actions | Usage |
| i)General Actions | |
| reduce(func) | Aggregate the elements of the dataset using a function func (which takes two arguments and returns one). |
| collect() | Return all the elements of the dataset as an array at the driver program. |
Pictorial view:
Example: Python spark:
Example: Scala spark:
3)count():
Returns number of elements in the RDD.
| Actions | Usage |
| i)General Actions | |
| reduce(func) | Aggregate the elements of the dataset using a function func (which takes two arguments and returns one). |
| collect() | Return all the elements of the dataset as an array at the driver program. |
| ii)Math/Statistical | |
| count() | Return the number of elements in the dataset. |
Example: Python spark:
Example: Scala spark:
4)first():
Return the first element in the RDD.
| Actions | Usage |
| i)General Actions | |
| reduce(func) | Aggregate the elements of the dataset using a function func (which takes two arguments and returns one). |
| collect() | Return all the elements of the dataset as an array at the driver program. |
| first() | Return the first element of the dataset. |
| ii)Math/Statistical | |
| count() | Return the number of elements in the dataset. |
Example: Python spark:
Example: Scala spark:
5)take(n):
Return an array with the first n elements of the RDD.
| Actions | Usage |
| i)General Actions | |
| reduce(func) | Aggregate the elements of the dataset using a function func (which takes two arguments and returns one). |
| collect() | Return all the elements of the dataset as an array at the driver program. |
| first() | Return the first element of the dataset. |
| take(n) | Return an array with the first n elements of the dataset. |
| ii)Math/Statistical | |
| count() | Return the number of elements in the dataset. |
Example: Python spark:
Example: Scala spark:
6)takeSample(withReplacement:boolean, num:int, [seed]):
Return an array with a random sample of num elements of the dataset, with or without replacement.
| Actions | Usage |
| i)General Actions | |
| reduce(func) | Aggregate the elements of the dataset using a function func (which takes two arguments and returns one). |
| collect() | Return all the elements of the dataset as an array at the driver program. |
| first() | Return the first element of the dataset. |
| take(n) | Return an array with the first n elements of the dataset. |
| ii)Math/Statistical | |
| count() | Return the number of elements in the dataset. |
| takeSample(withReplacement, num, [seed]) | Return an array with a random sample of num elements of the dataset, with or without replacement, |
Example: Python spark:
Example: Scala spark:
7)takeOrdered(n, [ordering]):
Return the first n elements of the RDD using either their natural order or a custom comparator.
| Actions | Usage |
| i)General Actions | |
| reduce(func) | Aggregate the elements of the dataset using a function func (which takes two arguments and returns one). |
| collect() | Return all the elements of the dataset as an array at the driver program. |
| first() | Return the first element of the dataset. |
| take(n) | Return an array with the first n elements of the dataset. |
| ii)Math/Statistical | |
| count() | Return the number of elements in the dataset. |
| takeSample(withReplacement, num, [seed]) | Return an array with a random sample of num elements of the dataset, with or without replacement, |
| iii)Set Theory/Relational | |
| takeOrdered(n, [ordering]) | Return the first n elements of the RDD using either their natural order or a custom comparator. |
Example: Python spark:
Example: Scala spark:
8)saveAsTextFile(path):
Save RDD as text file, using string representations of elements.
| Actions | Usage |
| i)General Actions | |
| reduce(func) | Aggregate the elements of the dataset using a function func (which takes two arguments and returns one). |
| collect() | Return all the elements of the dataset as an array at the driver program. |
| first() | Return the first element of the dataset. |
| take(n) | Return an array with the first n elements of the dataset. |
| ii)Math/Statistical | |
| count() | Return the number of elements in the dataset. |
| takeSample(withReplacement, num, [seed]) | Return an array with a random sample of num elements of the dataset, with or without replacement, |
| iii)Set Theory/Relational | |
| takeOrdered(n, [ordering]) | Return the first n elements of the RDD using either their natural order or a custom comparator. |
| iv)Data structure/ io | |
| saveAsTextFile(path) | Write the elements of the dataset as a text file (or set of text files) in a given directory in the local, HDFS or any other Hadoop-supported file system. |
Pictorial view:
Syntax:
saveAsTextFile(path,compresessioncode-class)Parameters:
- path – path to file
- compressionCodecClass – (None by default) string i.e. “org.apache.hadoop.io.compress.GzipCodec”
Example: Scala spark:
Since the default parallelism is 4, so during export, the RDD is split into fours partitions on local directory.
9)saveAsSequenceFile(path):
Write the elements of the dataset as a Hadoop SequenceFile in a given path in the local filesystem, HDFS or any other Hadoop-supported file system. This is available on RDDs of key-value pairs.
| Actions | Usage |
| i)General Actions | |
| reduce(func) | Aggregate the elements of the dataset using a function func (which takes two arguments and returns one). |
| collect() | Return all the elements of the dataset as an array at the driver program. |
| first() | Return the first element of the dataset. |
| take(n) | Return an array with the first n elements of the dataset. |
| ii)Math/Statistical | |
| count() | Return the number of elements in the dataset. |
| takeSample(withReplacement, num, [seed]) | Return an array with a random sample of num elements of the dataset, with or without replacement, |
| iii)Set Theory/Relational | |
| takeOrdered(n, [ordering]) | Return the first n elements of the RDD using either their natural order or a custom comparator. |
| iv)Data structure/ io | |
| saveAsTextFile(path) | Write the elements of the dataset as a text file (or set of text files) in a given directory in the local, HDFS or any other Hadoop-supported file system. |
| saveAsSequenceFile(path) | Saves RDD as sequencefile with key – value pairs |
Example: Python spark:
Example: Scala spark:
10)saveAsObjectFile(path):
Saves RDD as an object fil
| Actions | Usage |
| i)General Actions | |
| reduce(func) | Aggregate the elements of the dataset using a function func (which takes two arguments and returns one). |
| collect() | Return all the elements of the dataset as an array at the driver program. |
| first() | Return the first element of the dataset. |
| take(n) | Return an array with the first n elements of the dataset. |
| ii)Math/Statistical | |
| count() | Return the number of elements in the dataset. |
| takeSample(withReplacement, num, [seed]) | Return an array with a random sample of num elements of the dataset, with or without replacement, |
| iii)Set Theory/Relational | |
| takeOrdered(n, [ordering]) | Return the first n elements of the RDD using either their natural order or a custom comparator. |
| iv)Data structure/ io | |
| saveAsTextFile(path) | Write the elements of the dataset as a text file (or set of text files) in a given directory in the local, HDFS or any other Hadoop-supported file system. |
| saveAsSequenceFile(path) | Saves RDD as sequencefile with key – value pairs |
| saveAsObjectFile(path) | Saves RDD as an object file |
Example: Python spark:
Note:
Object file format does not support in python spark.
Example: Scala spark:
11)countByKey():Count the number of elements for each key, and return the result as a dictionary.
| Actions | Usage |
| i)General Actions | |
| reduce(func) | Aggregate the elements of the dataset using a function func (which takes two arguments and returns one). |
| collect() | Return all the elements of the dataset as an array at the driver program. |
| first() | Return the first element of the dataset. |
| take(n) | Return an array with the first n elements of the dataset. |
| ii)Math/Statistical | |
| count() | Return the number of elements in the dataset. |
| takeSample(withReplacement, num, [seed]) | Return an array with a random sample of num elements of the dataset, with or without replacement, |
| countByKey() | Returns a hashmap of (K, Int) pairs with the count of each key. |
| iii)Set Theory/Relational | |
| takeOrdered(n, [ordering]) | Return the first n elements of the RDD using either their natural order or a custom comparator. |
| iv)Data structure/ io | |
| saveAsTextFile(path) | Write the elements of the dataset as a text file (or set of text files) in a given directory in the local, HDFS or any other Hadoop-supported file system. |
| saveAsSequenceFile(path) | Saves RDD as sequencefile with key – value pairs |
| saveAsObjectFile(path) | Saves RDD as an object file |
Pictorial view:
Example: Python spark:
Example: Scala spark:
12)foreach(func):
To iterate through all the items in RDD and apply function to all.
Note:
Helpful, when we want to insert items in RDD.
| Actions | Usage |
| i)General Actions | |
| reduce(func) | Aggregate the elements of the dataset using a function func (which takes two arguments and returns one). |
| collect() | Return all the elements of the dataset as an array at the driver program. |
| first() | Return the first element of the dataset. |
| take(n) | Return an array with the first n elements of the dataset. |
| foreach(func) | Run a function func on each element of the dataset. |
| ii)Math/Statistical | |
| count() | Return the number of elements in the dataset. |
| takeSample(withReplacement, num, [seed]) | Return an array with a random sample of num elements of the dataset, with or without replacement, |
| countByKey() | Returns a hashmap of (K, Int) pairs with the count of each key. |
| iii)Set Theory/Relational | |
| takeOrdered(n, [ordering]) | Return the first n elements of the RDD using either their natural order or a custom comparator. |
| iv)Data structure/ io | |
| saveAsTextFile(path) | Write the elements of the dataset as a text file (or set of text files) in a given directory in the local, HDFS or any other Hadoop-supported file system. |
| saveAsSequenceFile(path) | Saves RDD as sequencefile with key – value pairs |
| saveAsObjectFile(path) | Saves RDD as an object file |
Example: Python spark:
Example: Scala spark:
Please click next to proceed further ==> Next