Hive Data Definition Language(DDL)- Tables
Hive Tables:In Hive, Tables are collection of data records which have same schema for all the records.
Note:
Hive Tables data stored in HDFS and Metadata (Schema of the table) stored in RDBMS.
Hive Table Types:
The below are sections which are going to try one by one:
Create Table
Create Table:
Syntax:
CREATE [TEMPORARY] [EXTERNAL] TABLE [IF NOT EXISTS] [db_name.]table_name
[(col_name data_type [COMMENT col_comment], ... [constraint_specification])]
[COMMENT table_comment]
[PARTITIONED BY (col_name data_type [COMMENT col_comment], ...)]
[CLUSTERED BY (col_name, col_name, ...) [SORTED BY (col_name [ASC|DESC], ...)] INTO num_buckets BUCKETS]
[SKEWED BY (col_name, col_name, ...)
ON ((col_value, col_value, ...), (col_value, col_value, ...), ...)
[STORED AS DIRECTORIES]
[
[ROW FORMAT row_format]
[STORED AS file_format]
| STORED BY 'storage.handler.class.name' [WITH SERDEPROPERTIES (...)]
]
[LOCATION hdfs_path]
[TBLPROPERTIES (property_name=property_value, ...)]
[AS select_statement];
Usage of arguments:
TEMPORARY – Specified for creation of temporary tables
EXTERNAL – Specified only for external tables
IF NOT EXISTS – Suppresses error messages when a table already exists with same name and ignores creation of table again even if there is a schema difference between existing table and new table.
db_name – Optional but can be used to specify the table under a target database, if we are not already working under it.
COMMENT – we can add comments to table as well as to columns (within single quotes) to provide descriptive information to users.
constraint_specification - to define primary or foreign key for the table
PARTITIONED BY – This clause is useful to partition the tables based on particular columns.
CLUSTERED BY – This clause is used to provide more structure to tables and partitions.
SKEWED BY – This clause is useful to create skewed tables.
ROW FORMAT – This clause is used to specify the format of each row in the input data.
Note:
If data fields are delimited by certain characters we can use DELIMITED sub-clause or we need to provide a SERDE that can serialize or deserialize the input data records.
Syntax for DELIMITED Clause:
row_format
: DELIMITED
[FIELDS TERMINATED BY char [ESCAPED BY char]]
[COLLECTION ITEMS TERMINATED BY char]
[MAP KEYS TERMINATED BY char]
[LINES TERMINATED BY char]
[NULL DEFINED AS char]
Default values of DELIMITED Clause:
Note:
Default field delimiter is Ctrl+A (octal representation – ‘\001’) (also represented as ^A),
Collection delimiter is Ctrl+B (‘\002’ or ^B)
Map keys are terminated by Ctrl+C (‘\003’ or ^C)
and lines terminated by new line feed ‘\n’.
Syntax for SERDE Clause:
row_format
:SERDE serde_name [WITH SERDEPROPERTIES (property_name=property_value, property_name=property_value, ...)]
STORED AS – Storage file format can be specified in this clause
Available storage file formats:
It is an alternative to above two clauses (ROW FORMAT & STORED AS) to provide custom row format handler class_name and custom serde properties.
LOCATION – Directory location for table data
TBLPROPERTIES – Metadata key/value pairs can be tagged to the table.
Sample TBLPROPERTIES:
TBLPROPERTIES ("comment"="table_comment")
TBLPROPERTIES ("hbase.table.name"="table_name") //for hbase integration
TBLPROPERTIES ("immutable"="true") or ("immutable"="false")
TBLPROPERTIES ("orc.compress"="ZLIB") or ("orc.compress"="SNAPPY") or ("orc.compress"="NONE")
TBLPROPERTIES ("transactional"="true") or ("transactional"="false") default is "false"
TBLPROPERTIES ("NO_AUTO_COMPACTION"="true") or ("NO_AUTO_COMPACTION"="false"), the default is "false"
TBLPROPERTIES ("EXTERNAL"="TRUE") , To change the managed table to external table vice versa.
AS select_statement – AS clause is used to create table similar to the schema of the select_statement and also know as CTAS (Create Table AS) clause.
Create Table Like:
LIKE clause with CREATE TABLE can be used to create tables similar to another existing tables or views.
Syntax:
CREATE [TEMPORARY] [EXTERNAL] TABLE [IF NOT EXISTS] [db_name.]table_name
LIKE existing_table_or_view_name
[LOCATION hdfs_path];
1.Managed and External Tables:
Basically two types of Hive tables:
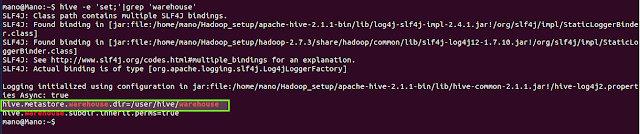
Note: A managed table is stored under the hive.metastore.warehouse.dir path property, by default in a folder path similar to /apps/hive/warehouse/databasename.db/tablename/
Example: Managed Table:
Dataset:
true|10|100|1000|10000|4.0|20.0|2.2222|1969-12-31 15:59:58.174|1970-01-01 00:00:00|hello|hello|k1:v1,k2:v2|100,200|10, "foo"
true|20|200|2000|20000|8.0|40.0|4.2222|1970-12-31 15:59:58.174|1971-01-01 00:00:00|||k3:v3,k4:v4|200,300|20, "bar"
Hive QL:
Output:
OK
managed_table.bool managed_table.ti1 managed_table.smi managed_table.in1 managed_table.bint managed_table.fl managed_table.db managed_table.dec managed_table.tms1 managed_table.tms2 managed_table.data1 managed_table.data2 managed_table.kmap managed_table.varay managed_table.str
true 10 100 1000 10000 4.0 20.0 2 1969-12-31 15:59:58.174 1970-01-01 00:00:00 hello hello {"k1":"v1","k2":"v2"} [100,200] {"c1":10,"name":" \"foo\""}
true 20 200 2000 20000 8.0 40.0 4 1970-12-31 15:59:58.174 1971-01-01 00:00:00 {"k3":"v3","k4":"v4"} [200,300] {"c1":20,"name":" \"bar\""}
Time taken: 0.109 seconds, Fetched: 2 row(s)
Web UI:
*External Tables:
hadoop@Mano:~$ hadoop fs -put '/home/hadoop/Mano/alltypes2.txt' /Mano/External_table
17/09/19 07:52:57 WARN util.NativeCodeLoader: Unable to load native-hadoop library for your platform... using builtin-java classes where applicable
Output:
hive> SELECT * FROM MANO_BB.EXTERNAL_TABLE;
OK
external_table.bool external_table.tiny1 external_table.smin external_table.dint external_table.bint external_table.fl external_table.db external_table.dec external_table.timest1 external_table.timest2 external_table.data1 external_table.data2 external_table.data3 external_table.dmap external_table.darr external_table.dstrc
true 10 100 1000 10000 4.0 20.0 4 1969-12-31 15:59:58.174 NULL string hello hello {"k1":"v1","k2":"v2"} [100,200] {"c1":10,"c2":" \"foo\""}
false 20 200 2000 20000 8.0 40.0 2 1970-12-31 15:59:58.174 NULL abcd world world {"k3":"v3","k4":"v4"} [200,300] {"c1":20,"c2":" \"bar\""}
Time taken: 0.916 seconds, Fetched: 2 row(s)
2.Storage/File Formats:
A file format is a way in which information is stored or encoded in a computer file. In Hive it refers to how records are stored inside the file.
Note:
File formats can be set on the property called hive.default.fileformat
Below are the some built in Hive formats:
Since it's TEXTFILE format , so can load any data files, either any text file,csv,tabs and JSON files,
Loading Data: which is of text file
hive> LOAD DATA LOCAL INPATH '/home/hadoop/Mano/employee.dat' OVERWRITE INTO TABLE TEXTFILE_FORMAT;
hive> SELECT * FROM TEXTFILE_FORMAT;
2)STORED AS SEQUENCEFILE
Sequence files are flat files consisting of binary key-value pairs.
Note:
Files are in the binary format which can be split and the main use of these files is to club two or more smaller files and make them as a one sequence file.
There are three types of sequence files:
SEQUENCEFILE format in Hive:
Syntax:
CREATE [TEMPORARY|EXTERNAL] TABLE IF NOT EXISTS DB_NAME.TABLE_ABLE(SCHEMA)
ROW FORMAT row_formats
STORED AS SEQUENCEFILE;
SEQUENCEFILE input and output formats from the following packages:
Hive, it verifies if the file format matches the table definition or not.
Example issue:
If we try to load the text file into SEQUENCE FILE FORMAT table in hive, returns an error
hive> LOAD DATA LOCAL INPATH '/home/hadoop/Mano/employee.dat' INTO TABLE SEQUENCEFILE_FORMAT;
FAILED: SemanticException Unable to load data to destination table. Error: The file that you are trying to load does not match the file format of the destination table.
Example:
Creating SEQUENCEFILE
Hive QL:
INSERT OVERWRITE TABLE SEQUENCEFILE_FORMAT SELECT * FROM TEXTFILE_FORMAT;
hive> SELECT * FROM SEQUENCEFILE_FORMAT;
WEB UI: RC FORMAT - 207B
4)STORED AS ORC:
ORC stands for Optimized Row Columnar which means it can store data in an optimized way than the other file formats.
ORC reduces the size of the original data up to 75%(eg: 100GB file will become 25GB).
Note:
As a result the speed of data processing also increases.
ORC format in Hive:
Syntax:
Hive has on it's packages, ORC input and output formats from the following packages:
Example issue:
IF we try to load the text file into ORCFILE FORMAT table in hive, returns an error
hive> LOAD DATA LOCAL INPATH '/home/hadoop/Mano/employee.dat' INTO TABLE ORC_FORMAT;
FAILED: SemanticException Unable to load data to destination table. Error: The file that you are trying to load does not match the file format of the destination table.
Example:
Creating RCFILE
Hive QL:
Loading Data: from another table or it should be binary file
LOAD DATA LOCAL INPATH '/home/hadoop/Mano/employee.dat' INTO TABLE ORC_FORMAT;
Other Tables:
1)Temporary Tables:
Note:
Temporary tables doesn’t support Partitioning & Indexing.
2)Skewed Tables:
Hive Tables:In Hive, Tables are collection of data records which have same schema for all the records.
Note:
Hive Tables data stored in HDFS and Metadata (Schema of the table) stored in RDBMS.
Hive Table Types:
The below are sections which are going to try one by one:
Create Table
- Managed and External Tables
- Storage Formats
- Row Formats & SerDe
- Partitioned Tables
- External Tables
- Create Table As Select (CTAS)
- Create Table Like
- Bucketed Sorted Tables
- Skewed Tables
- Temporary Tables
- Constraints
- Drop Table
- Truncate Table
Create Table:
Syntax:
CREATE [TEMPORARY] [EXTERNAL] TABLE [IF NOT EXISTS] [db_name.]table_name
[(col_name data_type [COMMENT col_comment], ... [constraint_specification])]
[COMMENT table_comment]
[PARTITIONED BY (col_name data_type [COMMENT col_comment], ...)]
[CLUSTERED BY (col_name, col_name, ...) [SORTED BY (col_name [ASC|DESC], ...)] INTO num_buckets BUCKETS]
[SKEWED BY (col_name, col_name, ...)
ON ((col_value, col_value, ...), (col_value, col_value, ...), ...)
[STORED AS DIRECTORIES]
[
[ROW FORMAT row_format]
[STORED AS file_format]
| STORED BY 'storage.handler.class.name' [WITH SERDEPROPERTIES (...)]
]
[LOCATION hdfs_path]
[TBLPROPERTIES (property_name=property_value, ...)]
[AS select_statement];
Usage of arguments:
TEMPORARY – Specified for creation of temporary tables
EXTERNAL – Specified only for external tables
IF NOT EXISTS – Suppresses error messages when a table already exists with same name and ignores creation of table again even if there is a schema difference between existing table and new table.
db_name – Optional but can be used to specify the table under a target database, if we are not already working under it.
COMMENT – we can add comments to table as well as to columns (within single quotes) to provide descriptive information to users.
constraint_specification - to define primary or foreign key for the table
PARTITIONED BY – This clause is useful to partition the tables based on particular columns.
CLUSTERED BY – This clause is used to provide more structure to tables and partitions.
SKEWED BY – This clause is useful to create skewed tables.
ROW FORMAT – This clause is used to specify the format of each row in the input data.
Note:
If data fields are delimited by certain characters we can use DELIMITED sub-clause or we need to provide a SERDE that can serialize or deserialize the input data records.
Syntax for DELIMITED Clause:
row_format
: DELIMITED
[FIELDS TERMINATED BY char [ESCAPED BY char]]
[COLLECTION ITEMS TERMINATED BY char]
[MAP KEYS TERMINATED BY char]
[LINES TERMINATED BY char]
[NULL DEFINED AS char]
Default values of DELIMITED Clause:
ROW FORMAT DELIMITED
FIELDS TERMINATED BY '\001'
COLLECTION ITEMS TERMINATED BY '\002'
MAP KEYS TERMINATED BY '\003'
LINES TERMINATED BY '\n'
Note:
Default field delimiter is Ctrl+A (octal representation – ‘\001’) (also represented as ^A),
Collection delimiter is Ctrl+B (‘\002’ or ^B)
Map keys are terminated by Ctrl+C (‘\003’ or ^C)
and lines terminated by new line feed ‘\n’.
Syntax for SERDE Clause:
row_format
:SERDE serde_name [WITH SERDEPROPERTIES (property_name=property_value, property_name=property_value, ...)]
STORED AS – Storage file format can be specified in this clause
Available storage file formats:
- SEQUENCEFILE
- TEXTFILE
- RCFILE
- PARQUET
- ORC
- AVRO
- INPUTFORMAT input_format_classname OUTPUTFORMAT output_format_classname
It is an alternative to above two clauses (ROW FORMAT & STORED AS) to provide custom row format handler class_name and custom serde properties.
LOCATION – Directory location for table data
TBLPROPERTIES – Metadata key/value pairs can be tagged to the table.
Sample TBLPROPERTIES:
TBLPROPERTIES ("comment"="table_comment")
TBLPROPERTIES ("hbase.table.name"="table_name") //for hbase integration
TBLPROPERTIES ("immutable"="true") or ("immutable"="false")
TBLPROPERTIES ("orc.compress"="ZLIB") or ("orc.compress"="SNAPPY") or ("orc.compress"="NONE")
TBLPROPERTIES ("transactional"="true") or ("transactional"="false") default is "false"
TBLPROPERTIES ("NO_AUTO_COMPACTION"="true") or ("NO_AUTO_COMPACTION"="false"), the default is "false"
TBLPROPERTIES ("EXTERNAL"="TRUE") , To change the managed table to external table vice versa.
AS select_statement – AS clause is used to create table similar to the schema of the select_statement and also know as CTAS (Create Table AS) clause.
Create Table Like:
LIKE clause with CREATE TABLE can be used to create tables similar to another existing tables or views.
Syntax:
CREATE [TEMPORARY] [EXTERNAL] TABLE [IF NOT EXISTS] [db_name.]table_name
LIKE existing_table_or_view_name
[LOCATION hdfs_path];
1.Managed and External Tables:
Basically two types of Hive tables:
- Managed Tables
- External Tables
*Managed Tables:
- Managed tables data is managed by Hive, moving data into its warehouse directory, configured via hive.metastore.warehouse.dir
Note: A managed table is stored under the hive.metastore.warehouse.dir path property, by default in a folder path similar to /apps/hive/warehouse/databasename.db/tablename/
- If managed table is dropped both data and metadata (schema) are deleted. i.e. these tables are owned by Hive.
- Less convenient to share with other tools like Pig, HBase etc, as these are maintained by Hive and data can be deleted without informing these tools
Example: Managed Table:
Dataset:
true|10|100|1000|10000|4.0|20.0|2.2222|1969-12-31 15:59:58.174|1970-01-01 00:00:00|hello|hello|k1:v1,k2:v2|100,200|10, "foo"
true|20|200|2000|20000|8.0|40.0|4.2222|1970-12-31 15:59:58.174|1971-01-01 00:00:00|||k3:v3,k4:v4|200,300|20, "bar"
Hive QL:
hive> CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS MANAGED_TABLE
> (
> BOOL BOOLEAN,
> TI1 TINYINT,
> SMI SMALLINT,
> IN1 INT,
> BINT BIGINT,
> FL FLOAT,
> DB DOUBLE,
> DEC DECIMAL,
> TMS1 TIMESTAMP,
> TMS2 TIMESTAMP,
> DATA1 STRING,
> DATA2 VARCHAR(5),
> KMAP MAP<STRING,STRING>,
> VARAY ARRAY<INT>,
> STR STRUCT<C1:INT,NAME:STRING>
> )
> COMMENT "EXAMPLE TABLE THAT USES ALL THE DATA TYPES OF HIVE"
> ROW FORMAT DELIMITED
> FIELDS TERMINATED BY '|'
> COLLECTION ITEMS TERMINATED BY ','
> MAP KEYS TERMINATED BY ':'
> STORED AS TEXTFILE;
OK
Time taken: 0.232 seconds
hive> LOAD DATA LOCAL INPATH '/home/hadoop/apache-hive-2.1.1-bin/examples/files/Done/alltypes.txt' INTO TABLE MANAGED_TABLE;
Loading data to table default.managed_table
OK
Time taken: 0.213 secondshive> SELECT * FROM MANAGED_TABLE;
OK
managed_table.bool managed_table.ti1 managed_table.smi managed_table.in1 managed_table.bint managed_table.fl managed_table.db managed_table.dec managed_table.tms1 managed_table.tms2 managed_table.data1 managed_table.data2 managed_table.kmap managed_table.varay managed_table.str
true 10 100 1000 10000 4.0 20.0 2 1969-12-31 15:59:58.174 1970-01-01 00:00:00 hello hello {"k1":"v1","k2":"v2"} [100,200] {"c1":10,"name":" \"foo\""}
true 20 200 2000 20000 8.0 40.0 4 1970-12-31 15:59:58.174 1971-01-01 00:00:00 {"k3":"v3","k4":"v4"} [200,300] {"c1":20,"name":" \"bar\""}
Time taken: 0.109 seconds, Fetched: 2 row(s)
Web UI:
*External Tables:
- External tables are not managed or owned by Hive and data will not be copied into hive warehouse directory but maintained at external location
- If external tables are dropped only the schema from metastore will be deleted but not the data files from external location.
- Provides convenience to share the tables data with other tools like Pig, HBase, etc…
- “Location” Clause is mandatory to create an external table
- If the structure or partitioning of an external table is changed, an MSCK REPAIR TABLE table_name statement can be used to refresh metadata information.
- Load or Make the data exist on hdfs at any other directory apart from hive warehouse,
hadoop@Mano:~$ hadoop fs -put '/home/hadoop/Mano/alltypes2.txt' /Mano/External_table
17/09/19 07:52:57 WARN util.NativeCodeLoader: Unable to load native-hadoop library for your platform... using builtin-java classes where applicable
hive> CREATE EXTERNAL TABLE IF NOT EXISTS MANO_BB.EXTERNAL_TABLE
> (
> BOOL BOOLEAN,
> TINY1 TINYINT,
> SMIN SMALLINT,
> DINT INT,
> BINT BIGINT,
> FL FLOAT,
> DB DOUBLE,
> DEC DECIMAL,
> TIMEST1 TIMESTAMP,
> TIMEST2 TIMESTAMP,
> DATA1 STRING,
> DATA2 VARCHAR(10),
> DATA3 CHAR(20),
> DMAP MAP<STRING,STRING>,
> DARR ARRAY<INT>,
> DSTRC STRUCT<C1:INT,C2:STRING>
> )
> ROW FORMAT DELIMITED
> FIELDS TERMINATED BY '|'
> COLLECTION ITEMS TERMINATED BY ','
> MAP KEYS TERMINATED BY ':'
> STORED AS TEXTFILE
> LOCATION '/Mano/External_table/';
Output:
hive> SELECT * FROM MANO_BB.EXTERNAL_TABLE;
OK
external_table.bool external_table.tiny1 external_table.smin external_table.dint external_table.bint external_table.fl external_table.db external_table.dec external_table.timest1 external_table.timest2 external_table.data1 external_table.data2 external_table.data3 external_table.dmap external_table.darr external_table.dstrc
true 10 100 1000 10000 4.0 20.0 4 1969-12-31 15:59:58.174 NULL string hello hello {"k1":"v1","k2":"v2"} [100,200] {"c1":10,"c2":" \"foo\""}
false 20 200 2000 20000 8.0 40.0 2 1970-12-31 15:59:58.174 NULL abcd world world {"k3":"v3","k4":"v4"} [200,300] {"c1":20,"c2":" \"bar\""}
Time taken: 0.916 seconds, Fetched: 2 row(s)
Note:
Even though if we drop the external table, the data will exist always,
2.Storage/File Formats:
A file format is a way in which information is stored or encoded in a computer file. In Hive it refers to how records are stored inside the file.
- As we are dealing with structured data, each record has to be its own structure. How records are encoded in a file defines a file format.
- These file formats mainly vary between data encoding, compression rate, usage of space and disk I/O.
Note:
- Hive supports both built-in and custom-developed file formats.
- Hive does not verify whether the data that you are loading matches the schema for the table or not. However, it verifies if the file format matches the table definition or not.
File formats can be set on the property called hive.default.fileformat
Below are the some built in Hive formats:
- STORED AS TEXTFILE
- STORED AS SEQUENCEFILE
- STORED AS RCFILE
- STORED AS ORC
- STORED AS AVRO
- STORED AS PARQUET
- STORED BY -- Need to check
- INPUTFORMAT and OUTPUTFORMAT -- Need to check
Let's discuss each one by one,
1)STORED AS TEXTFILE:
In Hive if we define a table as TEXTFILE it can load data of from CSV (Comma Separated Values), delimited by Tabs, Spaces, and JSON data.
Note:
TEXTFILE format is the default
TEXTFILE format in Hive:
Syntax:
CREATE [TEMPORARY|EXTERNAL] TABLE IF NOT EXISTS DB_NAME.TABLE_ABLE(SCHEMA)
ROW FORMAT row_formats
STORED AS TEXTFILE;
Note:
TEXTFILE input and TEXTFILE output format are present in the Hadoop package
org.apache.hadoop.mapred.TextInputFormat
org.apache.hadoop.mapred.TextOutputFormat
Example:
Creating TEXTFILE
Hive QL:
hive> CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS TEXTFILE_FORMAT
> (
> EMP_ID INT,
> NAME STRING,
> PRIMARY KEY(EMP_ID) DISABLE NOVALIDATE)
> ROW FORMAT DELIMITED
> FIELDS TERMINATED BY '|'
> LINES TERMINATED BY '\n'
> STORED AS TEXTFILE;
Since it's TEXTFILE format , so can load any data files, either any text file,csv,tabs and JSON files,
Loading Data: which is of text file
hive> LOAD DATA LOCAL INPATH '/home/hadoop/Mano/employee.dat' OVERWRITE INTO TABLE TEXTFILE_FORMAT;
hive> SELECT * FROM TEXTFILE_FORMAT;
2)STORED AS SEQUENCEFILE
Sequence files are flat files consisting of binary key-value pairs.
Note:
Files are in the binary format which can be split and the main use of these files is to club two or more smaller files and make them as a one sequence file.
There are three types of sequence files:
- Uncompressed key/value records.
- Record compressed key/value records – only ‘values’ are compressed here
- Block compressed key/value records – both keys and values are collected in ‘blocks’ separately and compressed.
SEQUENCEFILE format in Hive:
Syntax:
CREATE [TEMPORARY|EXTERNAL] TABLE IF NOT EXISTS DB_NAME.TABLE_ABLE(SCHEMA)
ROW FORMAT row_formats
STORED AS SEQUENCEFILE;
SEQUENCEFILE input and output formats from the following packages:
org.apache.hadoop.mapred.SequenceFileInputFormatNote:
org.apache.hadoop.hive.ql.io.HiveSequenceFileOutputFormat
Hive, it verifies if the file format matches the table definition or not.
Example issue:
If we try to load the text file into SEQUENCE FILE FORMAT table in hive, returns an error
hive> LOAD DATA LOCAL INPATH '/home/hadoop/Mano/employee.dat' INTO TABLE SEQUENCEFILE_FORMAT;
FAILED: SemanticException Unable to load data to destination table. Error: The file that you are trying to load does not match the file format of the destination table.
Example:
Creating SEQUENCEFILE
Hive QL:
hive> CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS SEQUENCEFILE_FORMAT(EMP_ID INT,NAME STRING)Loading Data: from another table or it should be binary file
> ROW FORMAT DELIMITED FIELDS TERMINATED BY '|'
> LINES TERMINATED BY '\n'
> STORED AS SEQUENCEFILE;
INSERT OVERWRITE TABLE SEQUENCEFILE_FORMAT SELECT * FROM TEXTFILE_FORMAT;
hive> SELECT * FROM SEQUENCEFILE_FORMAT;
3)STORED AS RC:
RCFILE is Record Columnar File which is another type of binary file format which offers high compression rate on the top of the rows.
RCFILE format in Hive:
Syntax:
CREATE [TEMPORARY|EXTERNAL] TABLE IF NOT EXISTS DB_NAME.TABLE_ABLE(SCHEMA)
ROW FORMAT row_formats
STORED AS RCFILE;
RCFILE input and output formats from the following packages:
RCFILE format in Hive:
Syntax:
CREATE [TEMPORARY|EXTERNAL] TABLE IF NOT EXISTS DB_NAME.TABLE_ABLE(SCHEMA)
ROW FORMAT row_formats
STORED AS RCFILE;
Example issue:
IF we try to load the text file into RCFILE FORMAT table in hive, returns an error
hive> LOAD DATA LOCAL INPATH '/home/hadoop/Mano/employee.dat' INTO TABLE RCFILE_FORMAT;
FAILED: SemanticException Unable to load data to destination table. Error: The file that you are trying to load does not match the file format of the destination table.
Example:
Creating RCFILE
Hive QL:
hive> CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS RCFILE_FORMAT(EMP_ID INT,NAME STRING)
> ROW FORMAT DELIMITED FIELDS TERMINATED BY '|'
> LINES TERMINATED BY '\n'
> STORED AS RCFILE;
Loading Data: from another table or it should be binary file
INSERT OVERWRITE TABLE RCFILE_FORMAT SELECT * FROM TEXTFILE_FORMAT;
RCFILE format in Hive:
Syntax:
CREATE [TEMPORARY|EXTERNAL] TABLE IF NOT EXISTS DB_NAME.TABLE_ABLE(SCHEMA)
ROW FORMAT row_formats
STORED AS RCFILE;
RCFILE input and output formats from the following packages:
org.apache.hadoop.hive.ql.io.RCFileInputFormat
org.apache.hadoop.hive.ql.io.RCFileOutputFormat
RCFILE format in Hive:
Syntax:
CREATE [TEMPORARY|EXTERNAL] TABLE IF NOT EXISTS DB_NAME.TABLE_ABLE(SCHEMA)
ROW FORMAT row_formats
STORED AS RCFILE;
Example issue:
IF we try to load the text file into RCFILE FORMAT table in hive, returns an error
hive> LOAD DATA LOCAL INPATH '/home/hadoop/Mano/employee.dat' INTO TABLE RCFILE_FORMAT;
FAILED: SemanticException Unable to load data to destination table. Error: The file that you are trying to load does not match the file format of the destination table.
Example:
Creating RCFILE
Hive QL:
hive> CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS RCFILE_FORMAT(EMP_ID INT,NAME STRING)
> ROW FORMAT DELIMITED FIELDS TERMINATED BY '|'
> LINES TERMINATED BY '\n'
> STORED AS RCFILE;
Loading Data: from another table or it should be binary file
INSERT OVERWRITE TABLE RCFILE_FORMAT SELECT * FROM TEXTFILE_FORMAT;
WEB UI: RC FORMAT - 207B
4)STORED AS ORC:
ORC stands for Optimized Row Columnar which means it can store data in an optimized way than the other file formats.
ORC reduces the size of the original data up to 75%(eg: 100GB file will become 25GB).
Note:
As a result the speed of data processing also increases.
ORC format in Hive:
Syntax:
CREATE [TEMPORARY|EXTERNAL] TABLE IF NOT EXISTS DB_NAME.TABLE_ABLE(SCHEMA)
ROW FORMAT row_formats
STORED AS ORC;
Hive has on it's packages, ORC input and output formats from the following packages:
org.apache.hadoop.hive.ql.io.orc
Example issue:
IF we try to load the text file into ORCFILE FORMAT table in hive, returns an error
hive> LOAD DATA LOCAL INPATH '/home/hadoop/Mano/employee.dat' INTO TABLE ORC_FORMAT;
FAILED: SemanticException Unable to load data to destination table. Error: The file that you are trying to load does not match the file format of the destination table.
Example:
Creating RCFILE
Hive QL:
hive> CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS ORC_FORMAT(EMP_ID INT,NAME STRING)
> ROW FORMAT DELIMITED FIELDS TERMINATED BY '|'
> LINES TERMINATED BY '\n'
> STORED AS ORC;
Loading Data: from another table or it should be binary file
LOAD DATA LOCAL INPATH '/home/hadoop/Mano/employee.dat' INTO TABLE ORC_FORMAT;
1)Temporary Tables:
- These are temporary and available till end of current session only.
- Useful in case of creating intermediate tables to copy data records from one table to another but can be deleted after our copy operation.
- Table’s data will be stored in the user’s scratch directory configured by hive.exec.scratchdir, and deleted at the end of the session.
Note:
Temporary tables doesn’t support Partitioning & Indexing.
2)Skewed Tables:
- Skewed tables to improve performance of tables with one or more columns having skewed (repeated) values.
- Hive will split the skewed (very often) values records into separate files.
- Skewed tables are not separate table types, it can be managed or external.
















Excellent article. Very interesting to read. I really love to read such a nice article. Thanks! keep rocking. Big data Hadoop online training India
ReplyDeleteThe main motive of the AWS big data consultant is to spread the knowledge so that they can give more big data engineers to the world.
ReplyDeleteThat is really nice to hear. thank you for the update and good luck. for more info
ReplyDeleteExcellent article. Very interesting to read. I really love to read such a nice article. Thanks! keep rocking. https://www.vanityliving.com/collections/side-tables-dubai-uae
ReplyDeleteI read your blog frequently and I just thought I’d say keep up the amazing work! ankara dil kursu
ReplyDeleteI went over this website and I believe you have a lot of wonderful information, saved to my bookmarks transfer file
ReplyDelete